Transvaginal Ultrasound
Overview
Ultrasounds are an important part of the evaluation of suspected gynecological pathology. It is an increasingly common medical test. They are used for a variety of reasons, from checking the health of an unborn baby to diagnosing problems with the reproductive or other organs.
This guide will focus on transvaginal ultrasounds: what they are, how they’re done, and what you can expect if you need one, what to expect on the day of the ultrasound, and what information can be gleaned from the examination. So, Let’s get started!
Everything You Need to Know About Transvaginal Ultrasound
What is a transvaginal ultrasound?
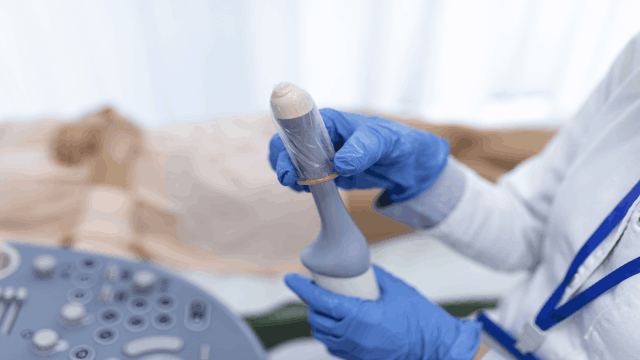
A transvaginal ultrasound is a type of pelvic ultrasound. It’s a diagnostic test that creates images of the inside of the vagina and pelvis. The test is performed with a small, hand-held device called a transducer. The transducer is inserted into the vagina, and it emits sound waves that bounce off organs and create echoes. These echoes are converted into electrical impulses that create images on a computer screen.
Transvaginal Ultrasound used to:
- Check for problems with the reproductive organs, such as ovarian cysts, endometriosis, or fibroids
- Evaluate the thickness of the lining of the uterus (endometrium)
- Screen for cancer of the ovaries, uterus, or endometrium
- Detect early pregnancy
- Guide needle biopsies
Sub Treatments For Ultrasound Services
We are one of the Best IVF Clinic in Delhi NCR!
51.8K
Subscribers
4.6 (383 reviews)
4.5 (409 reviews)
3.5 (254 reviews)

5 Out Of 5
How is a transvaginal ultrasound performed?
The test is performed in a doctor’s office, clinic, or hospital. You will be asked to lie on your back on an exam table with your feet in stirrups. A gel will be applied to the transducer and your vaginal opening. The transducer will be inserted into the vagina and moved around to get views of the organs from different angles. The images will be displayed on a computer screen. The procedure usually takes less than 30 minutes.
What should I expect on the day of the ultrasound?
You should expect to have a transvaginal ultrasound sometime during your pelvic exam. A gel will be applied to the transducer and your vaginal opening. The transducer will be inserted into the vagina and moved around to get views of the organs from different angles. The images will be displayed on a computer screen. The procedure usually takes less than 30 minutes.
What information can be gleaned from the examination?
A transvaginal ultrasound can provide important information about the health of your reproductive organs. It can help diagnose problems such as ovarian cysts, endometriosis, fibroids, or cancer. It can also help determine if you are pregnant and how far along you are in the pregnancy. The test is generally safe and well tolerated. Most women report only mild discomfort from the transducer being inserted into the vagina. Be sure to talk to your doctor if you have any questions or concerns about the test.
Transvaginal Ultrasoundare generally safe and well tolerated. Most women report only mild discomfort from the transducer being inserted into the vagina.
Be sure to empty your bladder before the ultrasound so that your bladder is not in the way of the view of the pelvis. You may be asked to hold your breath at certain points during the exam so that the image is not blurred. The images from the ultrasound will be stored so that they can be reviewed by your doctor and interpreted.
In some cases, a transvaginal ultrasound may be performed in real-time so that the doctor can see the organs and structures as they are being scanned. This is called a live scan. It is often used when there are concerns about ectopic pregnancy or when a biopsy of a mass is being done.
A transvaginal ultrasound is a painless and quick way to get important information about the health of your reproductive organs. Be sure to talk to your doctor if you have any questions or concerns about the test.
Patient Guide
Along with treating our patients, we also guide them with the help of our educational blogs and videos.
Educational Blogs
Why do blastocyst not implant?
The reasons for an unsuccessful implantation are very uncommon and rare as well. Blastocyst provides a greater chance of becoming pregnant therefore the procedure is handled properly as well.
What happens after blastocyst transfer?
Before jumping to the immediate question first let’s have a small brief of what is blastocyst transfer. Blastocyst transfer is the transfer of embryos that have achieved a higher stage of development.
Can blastocyst fall out?
Maximum patients worry about what they can do or cannot do after an embryo transfer. They have the fear that if they do something wrong, the embryo would not attach or fall out.
Educational Videos

What is TORCH test in infertility and why is it done?
There are numerous tests that are available to infertile couples that are recommended by some doctors, which might help them determine the cause of their infertility. One such test is the TORCH test.

What is Prolactin Hormone?
Prolactin is a hormone produced by the pituitary gland present at the brain’s base. It is best known for its role in lactation, or milk production, in breastfeeding women.However, Prolactin also plays other important roles in both men and women, such as regulating the immune system, stimulating the growth of new blood vessels, and influencing behaviour and reproductive function. In this blog, we will explore what Prolactin is, how it works, and what happens when there are imbalances in prolactin levels.

Frequently Asked Questions about Low AMH
Primordial and Preantral follicles produce AMH. So the AMH level indicates the number of eggs or egg reserves you have in your ovary. Putting simply, if your AMH level is low, then the number of eggs in your ovary is less.